Grand estimate what you need to know. Advantages of implementing a grand estimate system. Handing over work and certificates is a pleasure
Any construction of a facility begins with the preparation of design and estimate documentation. It's no secret that today, the need for manual work in any industry has disappeared. Numerous normative collections, a pencil and a calculator have been replaced by comprehensive estimate programs to help the cost estimate engineer.
One of such developments is GRAND SMETA. This is perhaps the most popular estimate program recently. Despite the fairly simple and understandable interface, initial training is required to work with Grand Estimate.
In order to become an estimator, the main thing, first of all, is to understand the construction technology of a particular facility, the sequence of work and the methods used. Knowing these basics, making an estimate will not be difficult. In addition, the automated estimate complex is adapted for almost all branches of construction.
The program has an extensive base for the repair and construction of individual structures. You can find the necessary information by typing in a search engine keyword and the program will automatically find and open the required collection. Now there is no need to sift through a bunch of literature, everything is much simpler and more effective.

In the prices themselves you can see not only the cost of individual works, but also a brief production technology. This is quite convenient for beginners. The only requirement for the program in order for it to work flawlessly is the correct entry of all initial coefficients.
Also, it will be necessary to take into account the construction site, climate zone, nature of the work and the season of work. All this is taken into account and written into the program manually. In case of the slightest error or unaccounted coefficient, the calculation result will be incorrect. That is why, when drawing up estimates, double control is required.
The program can work on the basis of territorial indices, as well as according to federal collections. The choice of one option or another depends entirely on the desires of the estimator or the requirements of the customer’s service. That is why indices for each calculation option are developed and approved in parallel with each other.
The option of working with estimates at current prices for building materials and services of workers and complex construction machinery has not been ruled out. This method is called resource-based. The estimator independently monitors the market and enters data into the program without taking into account conversion factors.

This allows you to calculate the cost of a facility under construction as accurately as possible without unwanted losses when converting from base prices to current prices.
So, the GRAND ESTIMATE software package allows you to reduce the time for preparing local estimates to a minimum, and calculate construction and individual structures with pinpoint accuracy.
A mobile version of the program recorded on a special device (flash key), which simultaneously serves as an electronic security key and a flash drive. In this case, the program does not require installation on a desktop computer and is launched directly from the flash key. The entire database of estimates is automatically saved to the same flash key during operation.
PC "GRAND-Smeta", version "Prof" with MINI key
A stationary version of the program that completely eliminates physical damage to the electronic key. This key can be effectively used in laptops, ultrabooks, and netbooks. The electronic key number is also engraved on the key itself.

Creation of all types of estimate documentation
Local estimates(estimates) - creation of estimates using the base, base-index, resource, resource-index, base-compensation methods. The ability to combine calculation methods in one document and compare the results.

Automatic generation of estimates based on work performed according to certificates
Automatic generation of estimates based on work performed according to work reports.

Object estimate calculations (estimates)
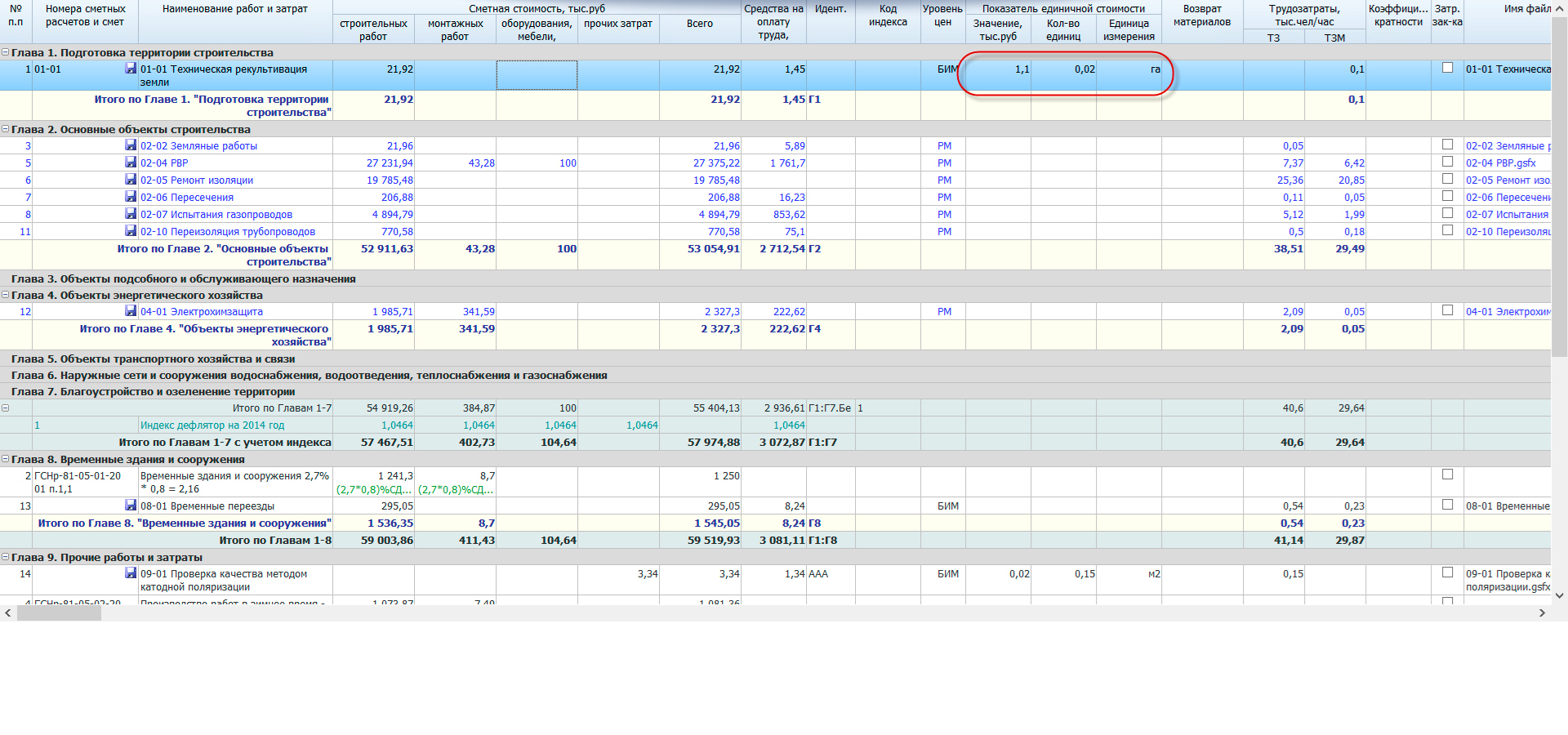
Object estimates (estimates), with the possibility of automatic creation based on local calculations compiled in the program. With automatic distribution of costs across chapters and synchronization of data when they change. Calculation of the unit cost indicator.
Filling positions with color and filtering by fill color
Filling positions with color with the ability to select a color from the palette, filtering by fill color.

Automatic creation of a summary resource statement
Automatic creation of a summary resource statement for selected acts of completed work. Formation of a statement of resources for the remainder of the work performed.

Macros
The ability to use external macros to change any data or parameters simultaneously in several estimates.

System Requirements:
- Free hard disk space of at least 2 GB + 200 MB for each regulatory framework;
- For the GRAND-StroyMaterials database – at least 15 GB;
- Operating system: Windows 8.1, 10 (64-bit).
(Server OS is not recommended for running the local version); - Processor not lower than 2GHz;
- RAM no less than 4 GB;
- CD reader (DVD-ROM);
- Screen resolution of at least 1280x800, number of screen colors at least 256;
- Free USB port;
In addition, the benefits of the program are:
- Formation of a log of completed work KS-6a;
- Automatic generation of a report on the consumption of basic materials (form M-29);
- A summary estimate of the cost of construction, with the possibility of automatic creation based on local, object-based calculations compiled in the program. With automatic distribution of costs across chapters and synchronization of data when they change. Calculation of unit cost indicator;
- Automatic generation of a statement of quantities according to the estimate based on local estimate data;
- Automatic creation of a resource list based on local estimate data;
- Formation of a consolidated resource statement;
- Material consumption report;
- Automatic calculation of the total cost by sections and by estimate;
- Introduction into the calculation of any taxes, duties, contractual and tender coefficients, including coefficients specific to the specific activities;
- Use for the calculation of GESN, FER, TER, any region, as well as OER and ISN with the possibility of linking to them indices by type of work, cost items and catalogs of average current estimated prices, developed by regional centers for pricing in construction;
- Automatic connection of additional estimate and normative databases, collections of conversion indices, catalogues, price tags, etc...
Key features of the program for calculating estimates “Grand Estimate”:
- Fully taken into account new order application of standards for overhead costs and estimated profits in construction in accordance with the letter of the State Construction Committee dated November 27, 2012 No. 2536-IP/12/GS.
- Drawing up and printing local calculations for design, construction, repair, installation and commissioning work on the basis of state (included in the register of the Ministry of Regional Development of Russia) and departmental standards.
- Formation of object estimates and summary estimates based on local estimates with import and grouping of data from local estimates.
- Convenient setup of additional charges and coefficients from the technical part of collections and MDS, automatic linking to unit prices of overhead costs and estimated profit standards, conversion indices to the current price level, automatic loading of basic and current prices for resources.
- Keeping records of work performed and drawing up reports for the required periods (per month, per period) with breakdown by items and materials.
- Formation, based on local estimates, Schedule plans necessary for planning the supply of various resources during the construction process (schedule, financing schedule and resource supply schedule).
- Drawing up a defective list (with printing) and a local estimate based on it.
- Formation of a statement of requirements for labor and material resources (for an object, for an estimate, for the amount of work performed; for several objects, several estimates).
- Separation of customer materials and returnable materials.
- Checking local estimates using forms No. 4 and No. 5.
- Conducting an examination of estimates: verification unit prices for compliance with regulatory frameworks, standards for overhead costs and estimated profits, checking indices of conversion to the current price level, base and current prices for resources. Automatic filtering of positions that did not pass the examination for one reason or another.
- Entering the physical volume of an item in natural units of measurement (taking into account the multiplicity factor of the meter in the price and to the volume).
- Adjusting the accuracy of physical volume values: you can set it and increase/decrease the accuracy.
- The ability to cancel completed actions and return canceled actions.
- Generating documents in MS Office and OpenOffice.org Calc formats
- Possibility of transferring estimates in PC “GRAND-Estimates”, XML or ARPS formats for exchanging estimates with other estimate programs.
The choice of professionals
Currently, the Grand Estimate software package is used by more than 90,000 estimators from 83 regions Russian Federation.
"GRAND-Smeta" is available in two formats:
- Standard version (requires installation)
- Portable version (no installation required)
Comprehensive regulatory framework
- The regulatory framework of the “Grand Estimates” includes all the information from the relevant collections of GESN and FER, TEP , SNiP - the technical part of the collections, the scope of work according to prices, standards for the consumption of material resources, etc. all editions of the GESN and FER database (Ministry of Regional Development of the Russian Federation 2009-2012 with amendments 1-8), FSNB-2014, TERcertifiedGosstandart of Russia.
- Integrated price standards for design solutions (NTsKR-2014) and integrated construction price standards (NTsS-2014) for transition from the prices of the base territorial area (Moscow region, Moscow) to the cost of construction for the constituent entities of the Russian Federation - taking into account the local price level and regional climatic conditions of construction.
- There is an automatic recalculation of estimates from one regional database to another, from TER to FER, from GESN to TER, etc. Convenient search for prices in the regulatory framework by justification, name, scope of work and name of resources included in the prices, search for text in the technical parts of collections.
- Collections for design and survey work (Tsentrinvestproekt, MRR database).
- Departmental collections (Gazprom, Russian Railways, RAO UES, Ministry of Culture, Petrochemistry, Transport, Energy, Transneft, Rosatom and many others). The ability to create personal, industry-specific regulatory frameworks tailored to the requirements and specifics of a particular Customer’s business.
Perfect compatibility
It doesn't matter which budgeting program you've used before. With us you can always upload or download into “Grand Estimate” (in XML, ARPS, Word, Excel format) estimates created in any other estimate program: Smeta.ru, Turbosmetchik, Hector, RIK, Smeta-Baghira, SmetaWizard, A0 , AROS, Gosstroysmet, 1C: Estimate and others.
Moreover: it was our company that exchanged data between Grand-Smeta and 1C, for which it received the corresponding 1C: Compatible certificate.
Handing over work and certificates is a pleasure
Certificate of conformity of the State Standard of Russia No. ROSS RU. SP11.N00054, GOSSTROY OF RUSSIA ISSUED 03/20/2003 by the certification body for software tools for mass use in construction (GP TsPS).
Certificate of official registration of the computer program No. 990629 was issued on August 27, 1999 by the Russian Agency for Patents and trademarks ROSPATENT
1. COMPOSITION OF THE SOFTWARE COMPLEX
— Drawing up and checking local estimates (forms 4.5)
— Accounting for the volume of work performed per month, per period, broken down by item and by material (form 2B, KS-2, form KS-3, form KS-6)
— Drawing up object estimates, summary estimates
— Calculation of the need for materials: for the completed volume of work, for the estimate
— Working with the regulatory framework
— Resource estimate, methods for calculating local estimates: resource, base-index
— Defective statement
2. COMPOSITION OF THE REGULATIVE FRAMEWORK OF 1984
— EREP collections
— Collections for repair work
— Price lists for materials 1-4 parts
— Price lists of wholesale prices for materials and equipment
— Collection “UralElectroMontazh” (UEM)
— Collections for commissioning works
— Price lists for equipment installation
— Price list of zonal estimated prices
— Catalogs for piece products
2.1 COMPOSITION OF THE NORMATIVE FRAMEWORK OF 2001 (for those who have a registration card for the user of the Base-2001)
— Collections GESN-2001, GESNr-2001, GESNm-2001, GESNp-2001, FER-2001, FERr-2001, FERm-2001, FERp-2001 All prices are tied to local conditions. It is possible to replenish the regulatory framework at the request of the Customer (free of charge)
— General instructions for EREP-84, VRER-84, TsMO-84, PN-84, STS-84
— Collection estimated standards additional costs during construction and installation work in winter time(ndz-84)
— General instructions for collections (technical part, Section 1)
— Rules for calculating the volume of work (technical part, Section 2)
— Coefficients for prices (technical part, Section 3)
— Estimated breakdown (according to linked collections)
— Material consumption (SNiP standards)
— Scope of work included in the price (according to ESN tables)
— Notes on pricing: wholesale prices (based on price tags for materials) gross weight (for materials)
4. WORKING WITH PRICES IN THE ESTIMATE POSITION
— Access to any information on pricing: general instructions for EPEP-84, BPER-84, TsMO-84, PN-84, STS-84 general instructions for the application of pricing, the procedure for determining the volume of work, estimate breakdown, material consumption rates, coefficients from technical parts, scope of work, notes
— Quick search for the required price in several collections: by justification, by name, by scope of work
— Application of coefficients to any element of the estimated decomposition when applying coefficients from the technical part, reference is made to the corresponding paragraph
5. THE SOFTWARE COMPLEX IS SETUP TO WORK WITH THE NORMATIVE FRAMEWORK GESN-2001, FER-2001, TER-2001
6. ADDITIONAL INFORMATION
6.1. Scope of delivery:
— instructions for working with the program
- CD
— electronic key Registered users of the programs are provided with free consultations on working with the program, re-delivery of the program in case of detection of defects, a guarantee of performance for the entire service life, the ability to download information from estimates compiled in other programs, such as “ABC-3RS”, “Cosmos” , “Estimate+”, “Bars+”, “ARS”, etc.
7. TECHNICAL REQUIREMENTS
7.1. Free hard disk space of at least 20 MB for one region
7.2. Processor Celeron 466 or higher
7.3. RAM from 64 MB.
An estimate is a calculation (document) that estimates the monetary and other costs of carrying out various works. Estimates are needed in absolutely all areas where it is necessary to calculate the amount of funds and more. Often, budgeting is a simple calculation necessary materials in pieces, kilograms, packages, etc.The calculation of estimates is most common in the construction industry. Strict control over costs, materials, etc. is especially important here. No construction contract can do without an estimate. The estimate is one of the most important documents. According to the estimate, the work performed is accepted and paid for. Following the estimate, all organizations plan capital investments for a certain period.
There are many types and varieties of estimates in the construction industry.
Free preparation of estimates is possible only with funding from private (commercial) sources, but most commercial firms still use the calculation of estimates for budgetary organizations, since, despite all the disadvantages Russian system There is simply no price formation or other price base for building materials, works, etc. in Russia.
First of all, the estimate is a very important document. The estimate must be approved with the contractor and the customer so that there are no difficulties in future cooperation. Based on the estimate, the courts resolve complex disputes between the contractor and the customer.
Estimates are calculated in 2001 prices in accordance with and on the basis of a collection of territorial estimate standards for determining the cost of construction and installation work.
When calculating estimates estimate documentation recalculated into current prices using indices of changes in the cost of the relevant work.
Types of estimates
Sometimes it is impossible to immediately calculate the estimated cost of large construction: over time, prices for raw materials, materials, tools, equipment, and labor increase. It is also impossible not to take into account the likelihood of force majeure, therefore, during the construction process, while the volume of work, and therefore the amount upcoming expenses are not completely determined, it is more convenient to use local estimate calculations. Based on them, object-based calculations of estimates are subsequently formed, where changes can be made as necessary. The preparation of estimates is carried out using estimate standards, which are available in special reference books.
The main purpose of local estimates is to determine estimated cost object under construction. Local estimate is an estimate document that covers types of work and costs, and estimates can be drawn up both for an individual object and for a specific type of work (construction of a foundation, roof, etc.).
An object estimate is a document containing all the information about the object under construction (repair) taken from local estimate calculations and local estimate documents.
A summary estimate of the cost of an object is compiled on the basis of object estimates for individual types of costs.
Estimating methods.
The resource method is most often used to prepare estimates. The cost is calculated using current (forecast) prices and tariffs (rates) of cost elements necessary to complete the work. Calculation of estimates is carried out on the basis of the following data: the need for materials, which is expressed in natural meters, the operating time of construction machines, labor costs of workers, consumption of energy resources used for technological purposes, etc. These resources are calculated on the basis of design materials and relevant regulatory sources ( reference books).
Another known method budgeting - base-index. It is based on the use of a system of current and forecast indices in relation to a value that has been determined at a reference price level (eg 2001 prices).
The resource-index method can also be used to prepare estimates. Its meaning is that cost estimates are calculated by combining the resource method mentioned above with the resource index system that is used in construction.
Another common method for preparing estimates is based on the use of data on the cost of similar objects built previously or reflected in the project.
What does any estimate consist of?
Much is determined by the type of work performed, the specifics of the facility, the capabilities of the contractor and other nuances, therefore, for example, the estimate for repairs and finishing of the clinic building will differ markedly from the construction estimate car parking or a shopping pavilion. In addition, the estimate that you draw up for your own needs will not be the same as the estimates officially used in construction and contracting organizations: it will most likely not contain many “formal” elements (names and addresses of the contractor, dates and estimates numbers, etc.). p.).
If you decide to start preparing estimates yourself, it will be useful to know what is included in a typical “official” estimate. Its elements are the following.
1. General information about the construction estimate. This data is located on the first (or title) page of the estimate and, as a rule, contains information about the contractor and the customer, the number and date of the estimate, its name (for example, “Estimate for the construction of a garage”), as well as details confirming the fact of approval of the estimate.
2. Section construction estimate. All information contained in it is grouped into appropriate thematic sections. This allows you to make the estimate clear and readable. Here are some typical examples of budget sections: “ Material resources", "Labor resources", " Repair work", "Finishing works", "Construction machines", etc.
3. List material assets are carried out by combining the resource method mentioned above with the resource index system that is used in construction., used during the work. For each item in the list, the following information is presented: the serial number in this section, the resource code according to the GESN directory (what the GESN directories are will be discussed). The site estimate is a document containing all the information about the object under construction (repair) taken from local estimate calculations and local estimate documents, name and unit of measurement of the material, its required quantity, price per unit of measurement and total cost of the material.
4. List of works according to this construction estimate. For each item in the list, the following information is presented: serial number in this section, code, name and unit of measurement of the work, their quantity, labor costs of workers and machinists (separately) in man-hours, average level of work or team of workers, tariff coefficient, wages of workers and machinists (separately) per unit of work and the total amount of wages of workers and machinists (separately) for the total volume of this work.
5. List of machines, mechanisms and devices necessary for carrying out work according to the current construction estimate. For each item in the list, the following information is reflected: serial number in this section, code, name of the machine (mechanism, device), unit of measurement for the operation of the machine (for example, machine hour). the number of units of operation required to produce the work, the price of the unit of operation and the cost of the item.
6. The total amount according to the estimate, and the size of the fund is indicated separately wages, the cost of materials used and the cost of operating machines (mechanisms, devices).
7. Various coefficients, allowances, discounts, overhead costs of the estimated profit, and other additional indicators, calculated as a certain percentage of the total amount of the construction estimate.
8. The amount of VAT, which is calculated from the final amount of the estimate, taking into account all additional indicators (coefficients, discounts, allowances, etc.).
9. The total amount of the construction estimate (line “Total”), taking into account additional indicators and VAT.
10. Last name, first name, patronymic and signature of the estimate preparer (estimator), as well as the person who checked the correctness of its preparation.
These elements in the compiled estimate are usually sufficient to create an overall picture construction work and calculating their cost.
 Lesson-study "Morphology
Lesson-study "Morphology Russian Church Slavonic dictionary online
Russian Church Slavonic dictionary online List of manual operations in 1 from 8
List of manual operations in 1 from 8